As we discussed in Part 1, Electronic reporting has become a need for companies. We have realized that this amazing function extends beyond report generation.
It allows for data exchange, such as importing bank statements or exporting data for external usage. We talked about the basic components and the way ER works with Dynamics 365 for finance and supply chain.
As we continue to part 2, we will be talking about further technical details on data mapping and working on the model mapping in it. Excited to learn? Let’s dive in!
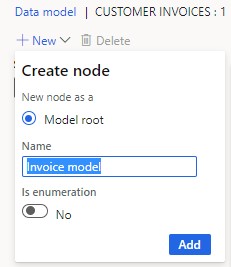
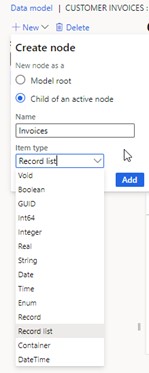
We talked about the data model, but we didn’t discuss the creation of the model. Here we are going to talk about the way to create a model.
How to Create a Model?
A single data model component can support numerous hierarchies of domain-specific business entities, as well as Dynamics 365 mappings that enable data flow for reports during runtime.
ER allows you to create tailored reports that fit unique business demands and regulatory requirements. The data model component’s unparalleled versatility and adaptability enable precise data administration and reporting.








Other Components of Electronic Reporting and their Configuration
We already talked about the root nodes and data model. Let’s move on to the Model mapping and Format configuration process in Detail.
Model Mapping
A data model component in ER describes the business target entity and attribute mappings along with the items needed to fulfill a certain reporting requirement.
Model mapping connects these data model components to the necessary application data sources in Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations, such as tables, fields, and views.
You can create and also opt for selecting mappings on a multiple level for various purposes and might refer to different areas of the data model.
In our example, we will develop a basic field mapping in Dynamics 365 that will connect our invoice header and lines to the customer invoice tables in Dynamics 365.
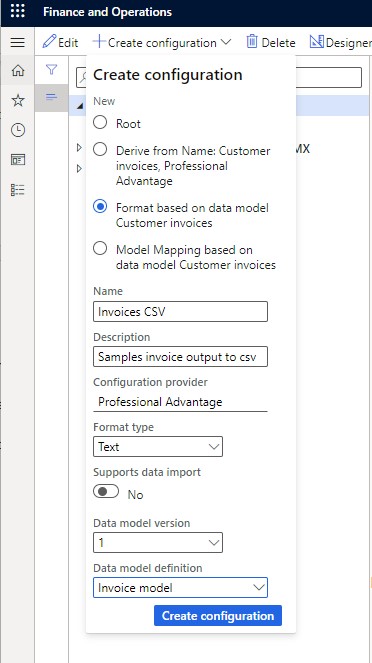
Create a model mapping
The data model is about the mapped entities and the source data in Dynamics 365 using the model mapping tool.





Format
The format component is defined as the structure and content of the runtime output file or the structure and content of the runtime imported document. It describes the data items that must be included in the output or incoming file, as well as the formatting and validation procedures.
The format component, in conjunction with the data model and model mapping components, defines the overall process for creating or processing electronic documents.
How to Create a Format?
The format component is defined as the structure and content of the runtime output file or the structure and content of the runtime imported document. It describes the data items that must be included in the output or incoming file, as well as the formatting and validation procedures.
The format component, in conjunction with the data model and model mapping components, defines the overall process for creating or processing electronic documents.






Bottom Line
Electronic Reporting is a magnificent tool offered by Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations for businesses. Its no-code capabilities, customization, and flexibility make it an exclusive tool that everyone can work with. We hope this comprehensive guide has given you a taste of what electronic reporting can do.
There are many more options to explore, including calculations, advanced record operations including grouping, controlling output destinations, business documents, and using ER for importing data and it is a long topic, maybe for some other time.
As for now, if you want to begin the use of electronic reporting using Dynamics 365, let the DHRP team help you with it. Reach out to get started today.